Crucial Insights: W-2 Employees and the Essential Tax Document
A W-2 employee, also known as a wage earner, is an individual formally employed by a company or organization. This classification entails receiving a W-2 tax each year, a crucial document for reporting income and taxes withheld. It is important to note that the distinction between W-2 employees and independent contractors or freelancers holds specific significance within the USA and may not align with employment practices in other countries.
Understanding the W-2 Tax Form
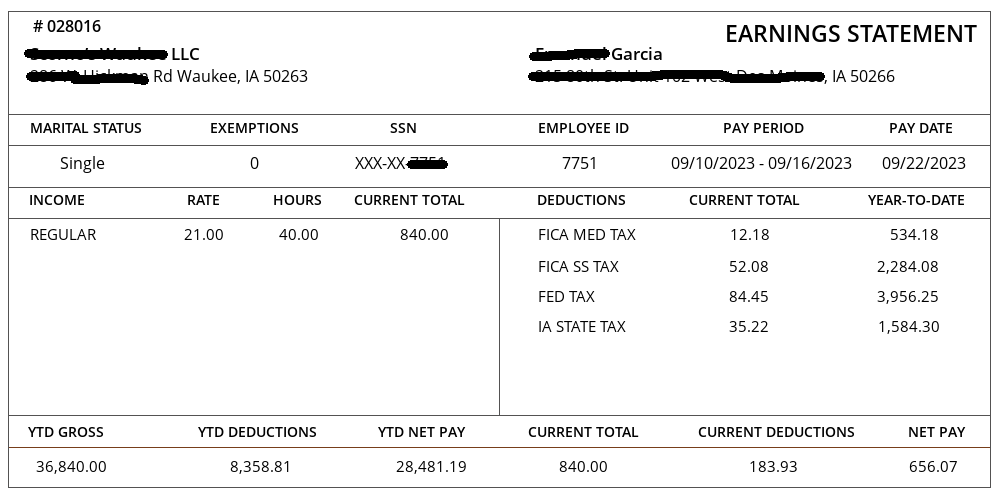
The W-2 tax form, officially known as the “Wage and Tax Statement,” serves as a comprehensive record detailing the income an employee received and the corresponding income tax withheld by the employer. Employers are responsible for furnishing a completed W-2 form to each W-2 employee on their payroll. Independent contractors, on the other hand, receive Form 1099 instead. W-2 employees utilize the information provided on this form when filing their annual tax return with the Internal Revenue Service (IRS). Click here to use w2 generator.
W-2 Employee Benefits
W-2 employees enjoy various benefits, both mandatory and optional, provided by their employers. These benefits contribute to the overall compensation package and may include:
- FICA taxes (Medicare and Social Security taxes)
- Worker’s compensation
- Health insurance, sometimes as a private plan
- Family and Medical Leave Act (FMLA) protections
- Disability insurance
- Retirement plans
These benefits add a significant layer of financial security for W-2 employees, as employers often contribute to taxes and provide coverage for various aspects of their well-being.
Getting a W-2 Form
Employers are required to issue W-2 forms to their employees by January 31st each year. If, for any reason, an employee does not receive a copy from their employer, they can contact the IRS for assistance. The IRS facilitates a process for employees to request copies of their W-2 forms.
Multiple Copies of W-2s
When it comes to W-2 forms, several copies are distributed to different entities:
Copy A: Sent to the Social Security Administration (SSA) by the tax deadline
Copy B: Kept by the employee for filing federal income tax returns
Copy C: Retained by the employee for personal records
Copy D: Held by the employer for their records
Copy 1: Filed by the employer with the state, city, or local department if required
Copy 2: Kept by the employee for state, city, or local tax filings, if necessary
Handling Multiple W-2s
Receiving W-2s from multiple employers is standard and poses no issues during the filing process. The tax filing platforms accommodate multiple W-2 entries seamlessly.
In the rare case of receiving multiple W-2 forms from the same employer, employees should verify with their employer to ensure accuracy. Duplicate forms may be intentional, such as due to business acquisitions, but identical forms may indicate an error.
To simplify the management of essential pay information, tools like paystub creator at Pay-stub.co empower users to preview W-2 form details before purchase, facilitating secure and efficient management of vital payroll information online.
